Introduction to Austria & Health Indicators
The Geography
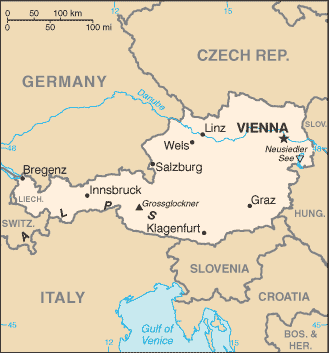
The exchange to Paracelsus Privatmedizinische Üniversität will take place in the cities of Salzburg and Linz, Austria. Austria, which is located in central Europe, is landlocked by 8 countries: Italy, Germany, Czech Republic, Hungary, Liechtenstein, Slovenia, Slovakia, & Switzerland. It measures at 83.871 sq km, which is around the size of the state Maine (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). A famous landmark are the Alps, which is located around the norther part of Austria, while its major river is the Danube (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). It has a variety of natural resources including oil, coal, lignite, timber, iron ore, copper, zinc antimony, magnesite, tungsten, graphite, salt and hydropower (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014).
Background
As of July 2015, the Central Intelligence Agency's (2014) Worldbook says the population of Austria is 8,665,550 people. The population consists mainly of Austrians with minorities such as the Yugoslavs, Turks and Germans (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). The official language is German (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). The capital is Vienna (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). It is considered a Federal Republic and consists of nine states: Burgenland, Kaernten (Carinthia), Niederoesterreich (Lower Austria), Oberoesterreich (Upper Austria), Salzburg, Steiermark (Styna), Tirol (Tyrol), Vorarlberg and Wein (Vienna) (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). It's currency is the Euro(Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). The predominant religion is Catholicisim(Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Its current president is Heinz Fischer and Chancellor Werner Faymann (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Presidents are elected every 6 years and can be eligible for a second term while the chancellor is picked by the president (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Faymann is the leader of the Social Democratic Party of Austria or SPOe (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014).
A Short History
Austria has an expansive history. Austria in German is Österreich, which translates to "the eastern land" (Beller, 2006, p. 10) This name was first found in historical sources dating to 996 AD, while the Latin name Austria, did not appear till 1147 AD (Beller, 2006). The Alpine mountain chain led to few early settlements, with the first evidence of culture during the late Iron Age around 800 BCE (Beller, 2006). The main group of the region were the Illyrians then to be displaced by Celts and the kingdom of Norcium (Beller, 2006). Due to pressure from northern Germanic tribes, the area joined the Roman Empire in 15 BCE for the next 500 years (Beller, 2006). King Otto I and the German army took hold of the land after fighting the Magyars and Bavarian rebels on 10, August 955 (Beller, 2006). This led to Otto to become the Holy Roman Emperor in 962 (Beller, 2006). The Babenburgs took power from 1000-1278 which led to increase in trades, cultivation of land and early German literature such as the Nibelungenlied (Beller, 2006). Leopold V, Duke of Austria, was the inspiration for the current Austrian flag (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). After Leopold fought in a bloody battle during the Third Crusade in 1191, his tunic was covered in blood (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). After removing his wide sash, it left behind a white band (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). However Austria's good fortune ended when Frederick II, also known as the Quarrelsome, took reign (Beller, 2006). When he was killed and had no heir crisis occured for decades till the Habsburgs took control (Beller, 2006). The Habsburgs ruled from 1278-1780 (Beller, 2006). It was under this family, the lands of Austria were acquisitioned (Beller, 2006). The Black Death occured during this reign in 1348 and 1349 (Beller, 2006). A distrust for the Jews in the area began around this time, believing they were at fault for the Black Death (Beller, 2006). Austria experienced its Age of Enlightenment under the rule of Joseph II, son of Maria Theresa and brother to Marie Antoinette, from 1764 to 1790 (Beller, 2006). His rule showed religious tolerance, legal reform and an increase in education, medicine and the arts (Beller, 2006). It was during this time Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart wrote his famous operas, Le nozze di Figaro and Die Zauberflöte (Beller, 2006). When Napoleon Bonaparte of France seeked to expand his empire (1792-1815), the Habsburgs dissolve leading to the Austrian Empire (Beller, 2006). Then in 1867, Emperor Franz Joseph unifies with Hungary making Austria-Hungary (Beller, 2006). In 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the hier to the Austria-Hungary throne, and his wife Sophie were assassinated by a Bosnian Serb in Sarajevo leading to the start of World War I (Beller, 2006). However with the end of World War I in 1918, so did the Habsburg Empire cease to be and Austria- Hungary is split (Beller, 2006). During this time, although Austria became a republic in 1920, Austria struggled to find an identity (Beller, 2006). Thus with Hitler's rise to power and promise for a economic and political success, Austria joins Nazi Germany in the Anschluss in 1936 and ceases to be Austria by 1938 (Beller, 2006). Austria began its deportation of Jews in 1941, acounting for the deaths of about three million Jews (Beller, 2006). At the end of World War II, Austria was divided by Soviet, British, U.S and French forces (Beller, 2006). Then in 1955, after the forces left, Austria gained its independence and declared neutrality (Beller, 2006). In 1995 Austria joined the European Union (Beller, 2006).
Austrian Health Indicators
Austria has a birth rate of 9.41 births for every 1,000 people and a death rate of 9.42 deaths per every 1,000 people (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Their current infant mortality is 3.45 deaths per 1,000 live births (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Life expectancy in Austria is 81.39 years for the total population, however the average for men is 78.76 and women, 84.15 years (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Austria uses 11% of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for health expenditures (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). There are 4.83 physicians for 1,000 people and 7.6 beds per 1,000 people (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). There is 100% drinking water source for total population as well as 100% sanitation facility access (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). A project put on by the World Health Organization and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, called the Global Burden of Disease (GBD), finds the top 5 reasons for premature death for 2010 were ischemic heart disease, stroke, lung cancer, self-harm and cirrhosis (Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 2015). The GBD found 8 of the 15 leading risk factors are dietary risks, smoking, hypertension, high body-mass index, physical inactivity, alcohol use, hyperglycemia, hypercholesteremia (Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 2015).
A Comparison to the United States
The United States of America has 12.49 births for every 1,000 people and 8.15 deaths for every 1,000 people (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). United states has a higher number of infant deaths with 5.87 deaths/1,000 live births (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Risks factors in the United States include dietary risks, high body-mass index, tobacco smoking, hypertension, hyperglycemia, hypercholesteremia and a sedentary lifestyle (Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 2015). Compared to Austria, the US has a higher percentage of obese people with 35% being obese, while 20.1% of Austrians are obese (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014). Similar to Austria, the number one cause of death in the United States is ischemic heart disease. The United States and Austria have similar dietary risks. A stunning finding is the United States utilizes 17.1% of their GDP, the most of any country, on health expenditures and yet is not considered to have the best healthcare system (Central Intelligence Agency, 2014).
Resources
Beller, S. (2006). A concise history of Austria. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Central Intelligence Agency. (2014). Austria. The World Factbook. Retrieved September 7, 2015, from https://ww.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/au/html
Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. (2015). Global Burden of Disease (GBD). Retrieved September 7, 2015 from www.healthdata.org
Module 2

Manuscript depiction (c. 1200) of Otto accepting the surrender of Berengar II of Italy. The headline reads Otto I Theutonicorum rex ("Otto the First, King of the Germans")

Illustration zum Nibelungenlied: "Wie Siegfried Chriemhilden zuerst ersah" by Eduard Julius Friedrich Bendemann (1811-1889) Retrieved from artstor.org

1945

Manuscript depiction (c. 1200) of Otto accepting the surrender of Berengar II of Italy. The headline reads Otto I Theutonicorum rex ("Otto the First, King of the Germans")